DHCP can also be cause of a problem in network. take the following steps to resolve the DHCP problem:
1- DHCP Server Must has a static IP moreover we Must authorize DHCP server to start in AD and also we need to active the scope.
a. Note: sometimes we need reauthorize or deactivate and reactivate the server for solving a problem.
2- If we faced with run out of addresses maybe we need to decrease the lease time so IPs release sooner.
a. Another reason for decreasing the lease time is when we changed some of our policy like IP range (check superscopes and migration in below) and we want changes take place as soon as possible.
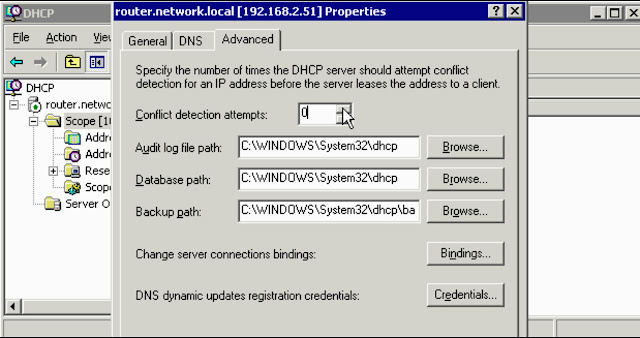
3- After a major DHCP failure when we don’t have backup we need to rebuild the scopes but in this time we must turn on Conflict Detection (before the server assigns an IP, It pings that IP to be sure that IP is not in use) for diagnosing the problems of DHCP we can check DHCP logs or check Network Monitor to make sure that server make DHCP Packet or not.
At the most attempts for major problems advised be 2
4- Sometimes wrong binding is an issue for DHCP server check Bindings that is showed in top figure, e.g.: if our server has several interfaces, which one want to give the service, does our external interface which is open to internet, is bound to DHCP? If it is bound uncheck it and just check the interface which is dedicated to give the dhcp service.
5- Sometimes it happened that a client plugged a device to the network which it has DHCP server on itself (like ICS/Internet Sharing) and it caused some problem in the network for that we can run DHCPLOC from support tools from win2k3 CD that shows location of DHCP.
6- Another issue is some internal firewalls(like ICF), Ensure UDP ports 67 and 68 are not blocked
7- In some scenario we see all clients from a switch cannot get IP from DHCP, we should check the switch has Broadcast Storm intelligent technology which blocks all broadcast enquiries or not.
8- DHCP for standalone server who are not members of domain called DHCPINFORM that they announce the presence of DHCP but as soon as other DHCP servers announce they give same scope service first one will stop leasing address
9- We cannot have two same DHCP Scopes on two servers because they overlap each other and that cause a server crash. So DHCP scope redundancy cannot be happened. But we can split a subnet between two segregate scopes and each server has one scope to lease addresses, in this case we can have both scopes in each server but we must activate one of them (cross purpose) and keep another one inactivated for redundancy purposes.
10- DHCP not only provides dynamic IP addresses for client computers but also it can bind/give a static IP address for specific MAC address such as Servers, Printers and other devices which need a static address. DHCP do that through Reservation in the scope what we do is just right-click on Reservation -> New Reservation-> put a reservation name, IP and MAC address(MAC address doesn’t need its hyphens)
11- DHCP can hold scopes for remote subnets, (we know DHCP is broadcast based and Routers block broadcasts) in this scenario we can do any of below solutions
a. Make routers to forward DHCP requests (some routers have BOOTP forwarding ability) to the DHCP server
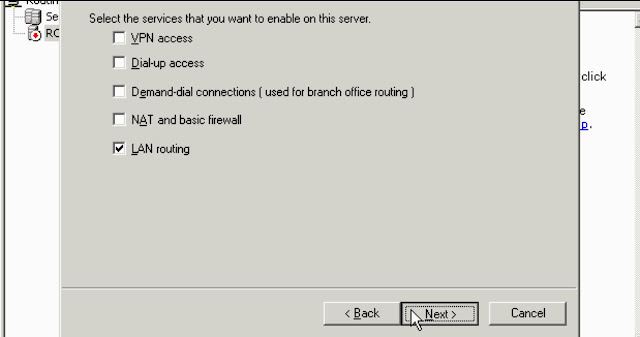
b. Configure a DHCP Relay Agent in remote subnets (DHCP Relay Agent included in Routing and Remote Access/RRAS) we should be aware that we must bind relay agent to an interface in RRAS because it somehow works as a bridge
c. DHCP Relay Agent installing:
Select the interface which is hearing to broadcast requests
DHCP Relay Agent is ready to giving service
12- Reconcile database scopes for fixing any inconsistencies
13- Backup from DHCP database
14- We can use NETSH command for scripting or managing DHCP by command line
Superscope: bring multiple scopes together for one physical network
15- If we want to use two logical subnet in one physical subnet (VLAN for decrease the impact of broadcast domain on network bandwidth) we need to make two segregate scope and associate the two scopes within one superscope then we need to have a router (or switch layer3) that can route between two subnets.
16- We can use superscopes for Migration goals, e.g.: we have an old class C scope and we need to make a new class B scope due to expanding the company, in this case we need to make a new class B scope and associate it with old scope under a superscope.
















0 Comments Received
Leave A Reply